There are two ways to edit a website; hard coding or using a content management system (CMS).
The former means to add content to a site one has to manually write the content into the source code. Now, this can be tedious, especially for non-coders. CMS to the rescue.
A CMS, also known as a Content Management System, is a system (software) that you incorporate into your website to manage and edit the site.
There are many other CMSs like Joomla, Drupal, Squarespace, and Wix, but WordPress is the most popular and old powering about 40% of the web.
Advantages of WordPress
Free
WordPress is Free and open source. Open source means it’s powered by the community. Coders from across the globe contribute to it’s features like the core functionality, themes and plugins.
Easy to use
WordPress is great for beginners and professionals. The user interface isn’t hard to grasp. It is pretty straight forward. Editing content is easy using the Rich Block Editor. You don’t have to write any HTML markup.
Community support
When picking a software (especially open source) you may want to go with ones with support if problems arise. Because of its popularity and contributions you’ll be able to find solutions to problems quickly.
SEO Friendly
WordPress makes SEO easy. WordPress automatically optimises some page elements best for search engines. For example, adding
Fast
WordPress automatically optimises image size by compression making a website faster. It also caches data.
How to install WordPress
WordPress can be installed automatically or manually.
Automatic Installation
When you buy web hosting most hosting services come with a control panel. These control panels differ from each hosting company. Cpanel is the most common with others like Direct admin and Plesk. Some hosting companies have their own built control panels.
Most of the control panels will have an option to install WordPress. In cpanel you can install WordPress via Softaculous.
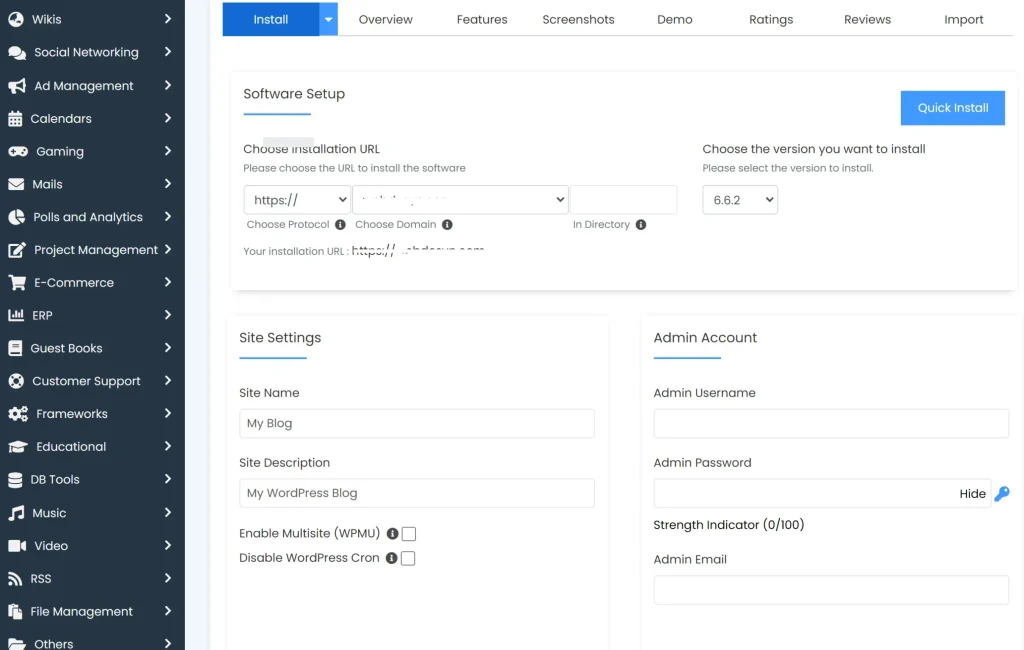
You’ll be asked the WordPress version, domain to use, username and password to use for logging into the dashboard.
You can state a subdirectory folder to install WP into if you don’t want to install it in the root directory.
WP Database Configuration
Database name: The database name you want to use. Don’t use spaces here instead use underscores. Also don’t use long database names. WordPress will create the database user and password for you. You can check these in the wp-config file.
Table prefix: The table prefix is a unique set of characters with which you’ll want to associate the WordPress tables. The default is wp_. Because you may have many tables the prefix allows you to distinguish between WordPress tables and non-WP tables.
WP Updates Configuration
You can enable auto updates of plugins, themes, or WordPress itself. I recommend disabling auto updates as incompatibility issues between new and old versions may arise. For example, your theme might be using outdated code which might be incompatible with a new WordPress version. This can cause the site to break.
WP Backups
Backups are good if your data is lost. Choose a backup routine and frequency (day, week, month).
After the backups, you can select a theme. You can change it later in the dashboard if you want
Manual Installation
Pages & Posts
You can add pages through Pages or Posts. There’s a difference between pages and posts in WordPress.
Pages are static while posts are dynamic. Examples of Pages are the About, Contact, or the Home page. This information is static and not updated frequently.
Posts on the other hand are dynamic and change often. They can be grouped into different categories or tags, unlike pages which only have Parent-Child relationships.
Create pages for your static content like Homepage, About, Contact, and Landing pages. Use Posts for your blog posts and written articles.
Media Library
The media Library contains all your uploaded files like images, videos and documents.
WordPress makes uploading files easy through drag and drop. You can upload files directly in the media library or in other places where attachments are allowed like in Posts and widgets etc.
WordPress themes & appearance
WordPress themes dictate how the website looks and functions. They include colours, fonts, style, layout and many other things.
Choose a theme based on your needs. There are many free themes on the web. Most common themes will have a header, sidebar, main content, and footer.
Plugins
Plugins in WordPress are add-on software that enhance a site. As your site grows you’ll need other functionalities that the core WordPress cannot provide. Some good plugins to have are SEO plugins like Yoast or AIOS (All In One SEO), Jetpack or Litespeed for site speed and optimisation.
Keep plugins at a minimum. Don’t install too many plugins as they can slow a website or make debugging a nightmare if problems arise.
WordPress Settings
Here you can adjust site settings like URL structure, image resizing, page to use as the Homepage, dashboard appearance etc.
WordPress Users
The user’s page is where you add and delete people who can access the WordPress Dashboard. You can assign roles to people you add like Author, Editor, Admin or Subscriber.
Tools
The Tools section gives you the ability to import or export a WordPress site.
These are the sections that WordPress comes with by default. As you install other plugins and themes more pages and sections will be added.

