If you don’t have a content management system like WordPress it means you have to manually create HTML files, write html markup and upload as a web page. This can be a daunting process especially for a layman without coding knowledge.
CMSs help to create pages easily without writing HTML markup. Page content is written in a WYSIWYG (What Your See Is What You Get) editor enabling HTML formatting with a click of a button.
What are Pages in WordPress
A WordPress page is a static and singular piece of content. Static means the content doesn’t change often. You may want to use pages for your Homepage, About, Contact, and Service pages.
Page hierarchy
Pages are usually singular or have a one way hierarchy – Parent-Child. You can make a page a child of another by assigning it to a parent page like below.
WordPress Posts
WordPress posts are a type of page but dynamic. They can be grouped into certain categories. Unlike pages which only have a one way, parent-child hierarchy, posts can be assigned to many categories.
The content in Posts usually changes often.
Posts are suitable for blog posts and articles where you’ll want some sort of categorisation. For example, suppose you want to write construction articles you may want to group these into different categories like Residential, Roads & Commercial.
Post taxonomies (categories & tags)
WordPress taxonomies are ways of grouping posts.
We’ve talked about grouping posts, and categories and tags are the default ways you can use to group posts in WordPress.
Categories are hierarchical and can be nested meaning you can create sub-categories, sub sub-categories and so on.
Tags, however, are standalone groupings and have no relationship whatsoever. Use tags for more descriptive and specific groupings. For example, using the construction articles above you can assign tags like cottage housing, double storey etc.
Classic vs Block Editor
WordPress allows easy editing of text into HTML format. WordPress has two editors; classic and block. The Block editor is the new and modern editor with robust features.
The block editor has more control on the styling of HTML elements unlike the classic editor which only gives the bare minimums.
If you want to use the classic editor you have to install the Classic Editor plugin. You may find the classic editor in other post types, e.g Woocommerce products.
Post/page info section
Status
The status of the page/post whether published or draft. The values are Published, Draft, Pending for Review, Private for admins only, Scheduled, or Password protected. A draft page/post will not go live until you publish it. Users will not see drafts.
Visibility
Privacy sets who is able to view the pages/posts; public for all people, private for admin viewing only or password-viewing only. Note this is only visible in the Classic Editor. These options are put together under Status & Availability in the Block editor
Link/URL slug
The URL slug is the last part of the URL. This option allows you to set a custom URL endpoint. By default WordPress will use the page/post title for the URL slug. It will remove all non-alphanumeric characters and replace spaces with hyphens.
Author
The author/writer of the page/post
Date
The date the page/post was last updated.
Parent
For pages only, this allows you to make the current page a child of another page by assigning a parent.
Page Template
Depending on your theme you can select a custom template to render the page. These custom templates are usually different from the default page display.
Sticky Posts
Making a post sticky allows it to display on top of the front page or category and tag archive pages. In the Classic editor it is under Visibility.
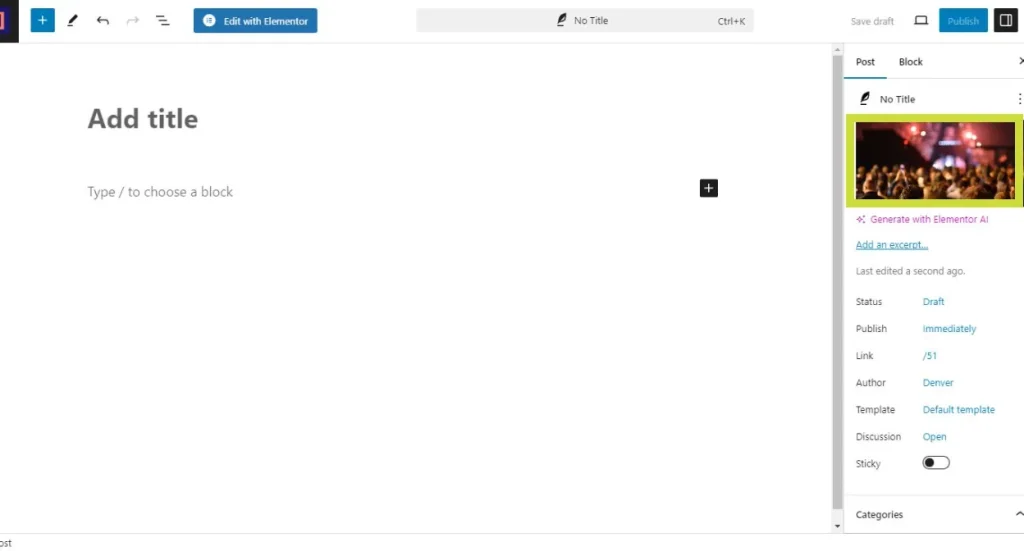
Featured images
A featured image is an attached page/post photo that will typically show in archive pages like categories or tags. Depending on the theme this image can be used as the hero image displayed on top of a post/page content.
Post Excerpt
A post excerpt is a short summary of the actual post content. This is optional. If you don’t write a custom excerpt WordPress will use the first paragraph words as the excerpt.
Sticky Posts
Custom Meta
Sometimes you may want to add additional information to a post/page to render to users. You can use custom meta fields which are name-value pairs of data.
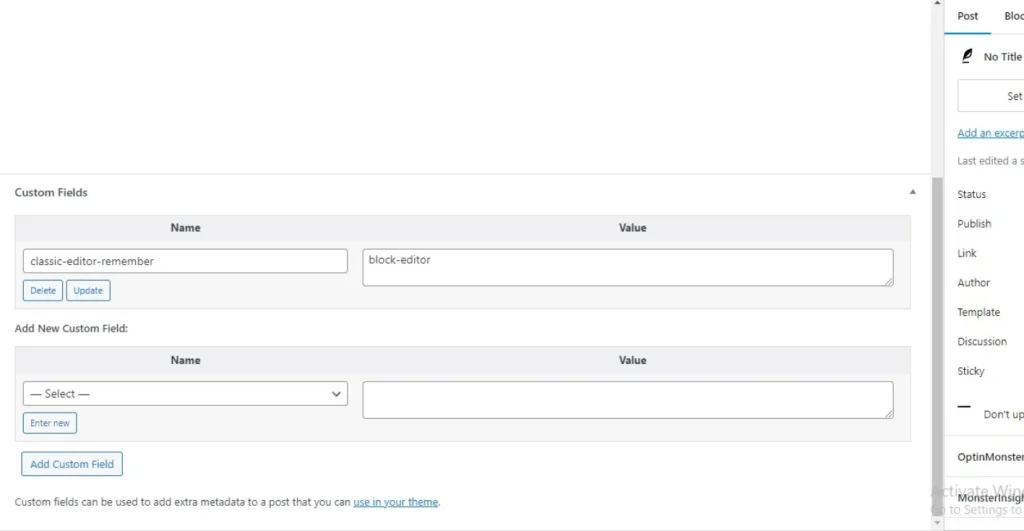
The custom meta interface is disabled by default. In the Block editor activate it by clicking the 3 dots in the top ight corner. Go to Preferences. Under General scroll to the bottom and check Custom fields.
In the Classic editor, click Screen options and check Custom Fields.
Options & Settings
Options enable you to adjust the editor settings like viewing mode, editing type (code/visual), preferences and many others. Click the 3 dots in the top-right corner.

