In the root folder of your website installation there’s a file called wp-config. php which holds some Important information needed for the website to function.
Database Configuration
The WP config file holds the database credentials. These credentials are defined as follows:
DB_NAME
The name of your database. You can find this in your control panel or phpmyadmin
DB_USER
The username of the database
DB_PASSWORD
The database password
DB_HOST
The database host name. Typically the value is localhost referring to the local server itself. The port number can be attached to the end of the host after a semicolon like so
define( ‘DB_HOST’, ‘mysql.example.com:3307’ );
The default port for MYSQL is 3306 and can be left out.
DB_CHARSET
The database character set. Default is UTF-8
DB_COLLATE
The database collation type.
Keys & Salts
This section has all the WordPress unique keys and salts for authentication and hashing. You can use your generated salts or keys. Yu can generate them here, WordPress.org secret-key service
Other Constants
WP_DEBUG
This value when set to true will display all website errors on the frontend.
Thge table_prefix variable stores the unique prefix of WordPress tables
How to edit the WP config file
You can edit the WP config file by opening it through a FTP file manager like Filezilla. You need to know the path where website files are stored. Typical directories are: public_html, domains/site_name
If your site is in a subdirectory you must navigate to that directory.
Right click the file in FileZilla and click Edit. Press Ctrl+S on Windows or Command+S on Mac to save your edits.
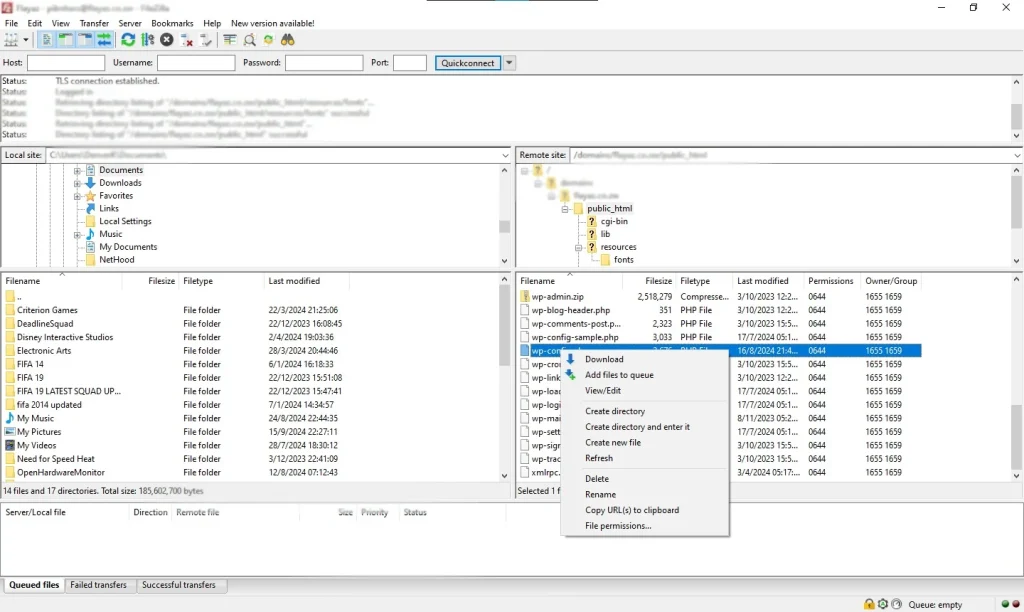
You can use the file manager in your Control panel

